Document status: Work in progress
"Trust" as umbrella term
In search of an umbrella term for the frameworks that shall assure information security and privacy the term trust seems to be suitable. It is vague enough to span many concepts, and useless enough to dispensable for specific meanings.
...
Guinnane “argues that […] the concept is, at least for economic questions, superfluous: the useful parts of the idea of trust are implicit in older notions of information and the ability to impose sanctions”. [Guinnane2005]. In particular legislation does not rely this term.
Decomposing trust
The purpose of this model is to define a set of specific terms that together are more reliable than a definition of trust.
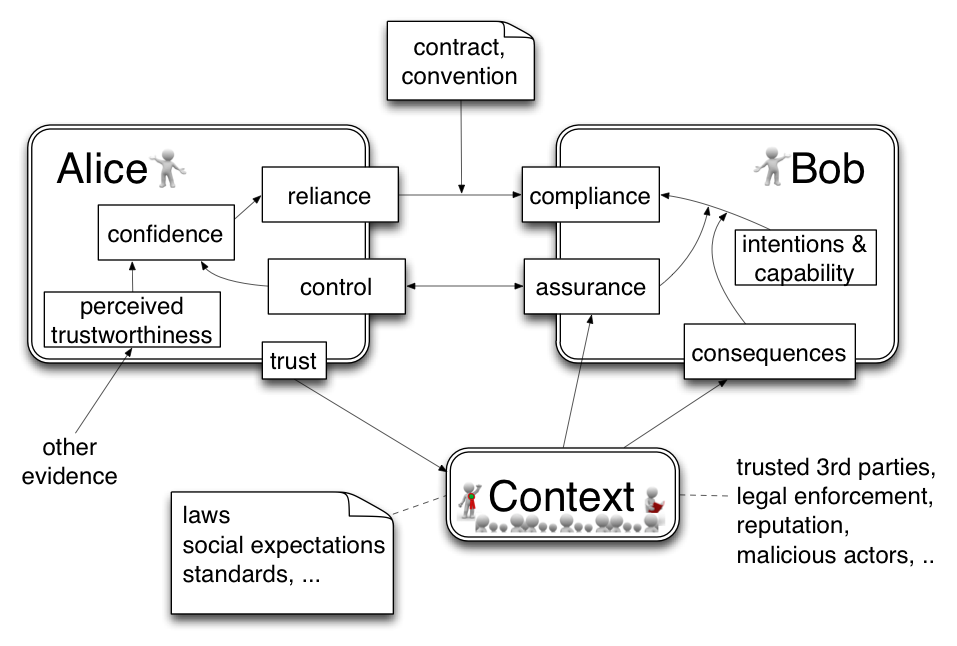
The baseline model: Alice trusts Bob
Alice wants to engage in a transaction with Bob, and has some expectations regarding Bob’s handling of Alice’s risk exposure. Bob acts independently and his intentions may be driven by self-interest or other forces and not be fully aligned with Alice’s expectations. This simple model shows how the behavior of Alice and Bob is driven by internal and external factors:
Alice’s reliance on Bob is driven by her confidence, which might range from low to high. The confidence is an internal assessment based on factual control and perceived trustworthiness, which consists of soft factors like “I always trust properly dressed and polite bank tellers” or “In the Internet I shop only with big global brands”.
...
If Alice would be a paranoid control freak, no perceived trustworthiness would be assumed from Bob, even 3rd party root trust would be minimized. In that scenario transactions would be very difficult. At the other extreme, if Alice would relinquish all control, chances are high that some naïve assumptions about Bob’s willingness and competence would be disappointed.
Definitions
Assurance part of a management system focused on providing confidence that requirements will be fulfilled[1|#_ftn1].
Note: In line with the Oxford English Dictionary definition assurance is a declaration and does not imply consequences and enforcement.
...
Reliance is the confident behavior towards a trusted party.
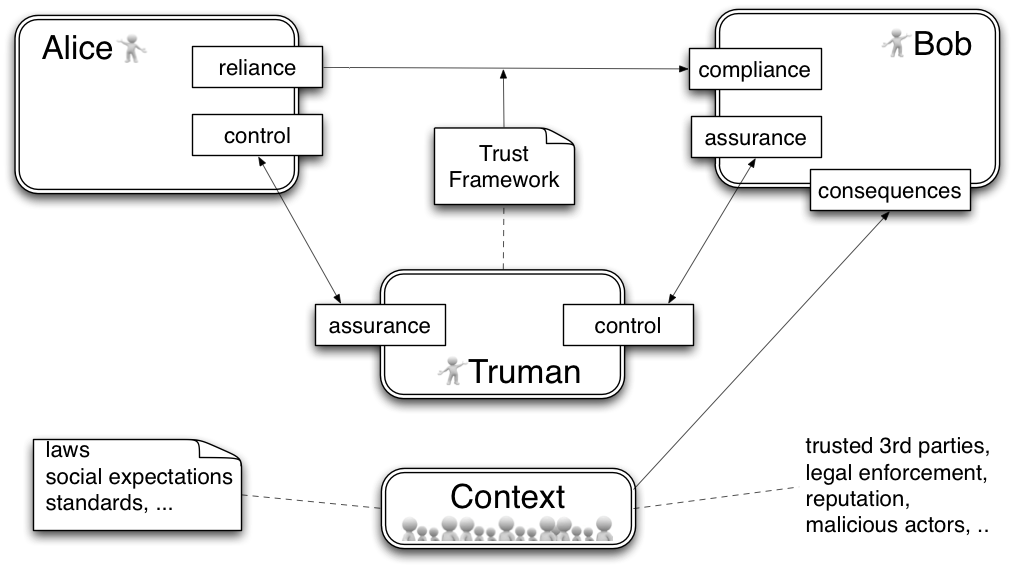
The third party model: Beyond bilateral trust
In contrast to the baseline model that is suitable for 1:1 relationships, Internet-scale federations have to deal with massive amounts of users, a variety of use cases and multiple jurisdictions. Moreover, Bob might be a human, device or network. To conquer this complexity brokered trust is essential. This model also simplifies actors by not trying to have an inner model, but only regard their "interfaces".
Definitions
(these definitions are work in progress!)
...
- Assurance of the link of a digital identity credential to a real-world identity (Authenticity)
- Compliance with security objectives for integrity, confidentiality and accountability of the communication
- Adherence to the privacy policy of the PII controller
- Fulfillment of a defined service level (e.g. short- and long-term availability of credentials and services)
- User control over own data (like availability for export in an open format)
Identity Trust Framework
The term Identity in Identity Trust Framework is suggested because most security objectives are to proof identity to a Relying Party. However as mentioned above in “Identity Assurance vs. Assurance” this is too restrictive as it excludes objectives like data protection, privacy and user control.
Therefore I think that Infrastructure Trust Framework or just Trust Framework would be a better term.
References
[Cofta2007] Piotr Cofta. Trust, Complexity and Control: Confidence in a Convergent World. John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
[Guinnane2005] Timothy W. Guinnane. Trust: A Concept Too Many. http://ssrn.com/abstract=680744
...
[1|#ftnref1] Derived from _Quality Assurance in ISO/IEC 9000:2005
...